SSL Certificate
Secure Every Click
✔️ Secure your website
✔️ Protect your data
✔️ Build trust

SSL Certificate
Secure Every Click
✔️ Secure your website
✔️ Protect your data
✔️ Build trust

Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) certificate
provides a secure connection by encrypting data between your website and its visitors.
Why SSL ?
Transmits data in plain text, exposing it to attackers.
Vulnerability to Attacks
Modern browsers flag HTTP as "Not Secure."
SEO Penalty - Lower rankings on search engines.
Increases the chances of sensitive information being stolen.
Encrypts data to protect sensitive information from interception.
Builds Trust and Credibility.
Preferred by search engines, leading to higher rankings in SEO.
Guards against eavesdropping and MITM attacks.
Meets industry standards for handling sensitive data



An Secure Sockets Layer - SSL certificate provides a secure connection by encrypting data between your website and its visitors.
It ensures the safety of sensitive information such as passwords, credit card details, and personal data, while also enhancing trust with a visible padlock and HTTPS in the browser address bar.
Ideal for businesses of all sizes, SSL certificates are essential for protecting online transactions and boosting your website's credibility.
Transmits data in plain text, exposing it to attackers.
Vulnerability to Attacks
Modern browsers flag HTTP as "Not Secure."
SEO Penalty - Lower rankings on search engines.
Increases the chances of sensitive information being stolen.
Encrypts data to protect sensitive information from interception.
Builds Trust and Credibility.
Preferred by search engines, leading to higher rankings in SEO.
Guards against eavesdropping and MITM attacks.
Meets industry standards for handling sensitive data


We’re moving towards a more secure web by strongly encouraging HTTPS for all sites.
- Google Chrome Security Team -
We’re moving towards a more secure web by strongly encouraging HTTPS for all sites.
- Google Chrome Security Team -
Enhanced Security and Regulatory Compliance
SSL secures data transfer on your site, protecting passwords and credit card details.
Comply with GDPR and PCI DSS to safeguard sensitive data
Establish Trust Showcases your dedication to security, boosting user confidence in your site.
Boosted by search engines for better rankings

Optimize the website's presence in search engine rankings
Higher Click-Through Rates
Reduced Bounce Rates as browsers mark HTTP sites "Not Secure," driving users away.
Builds Trust and Credibility
Boosts trust with a secure padlock icon and "https://" in the address bar
Essential for online transactions as customers need secure connections
Cyberattack Protection
Prevents Eavesdropping
Defends Against MITM Attacks
Authenticates Your Website
Protects Sensitive Data
Enhanced Security and Regulatory Compliance
SSL secures data transfer on your site, protecting passwords and credit card details.
Comply with GDPR and PCI DSS to safeguard sensitive data
Establish Trust Showcases your dedication to security, boosting user confidence in your site.
Boosted by search engines for better rankings
Optimize the website's presence in search engine rankings
Higher Click-Through Rates
Reduced Bounce Rates as browsers mark HTTP sites "Not Secure," driving users away.


Builds Trust and Credibility
Boosts trust with a secure padlock icon and "https://" in the address bar
Essential for online transactions as customers need secure connections
Cyberattack Protection
Prevents Eavesdropping
Defends Against MITM Attacks
Authenticates Your Website
Protects Sensitive Data

How SSL protect your website?
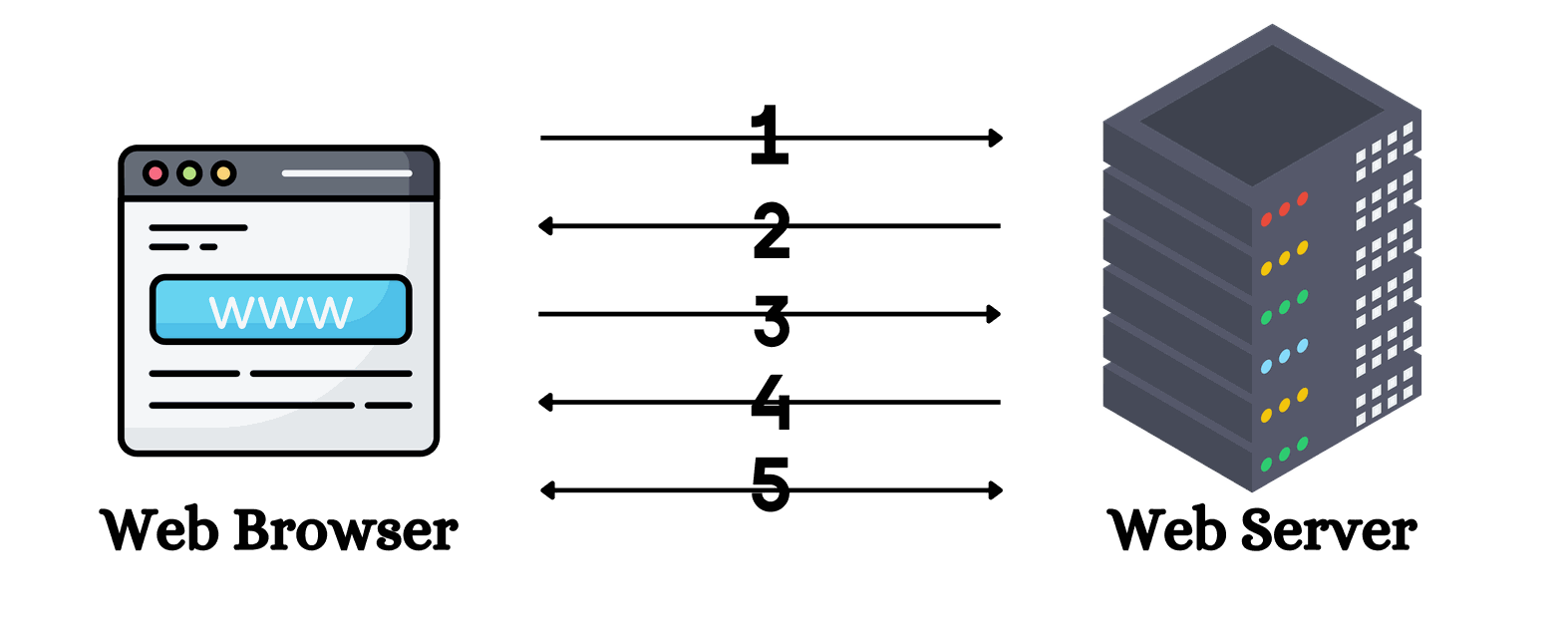
1. The browser connects to an SSL-secured web server and requests identification.
2. The server sends its SSL Certificate, including the public key.
3. The browser encrypts and sends a symmetric session key back to the server using the public key after checks the certificate with trusted CAs for validity.
4. The server decrypts the session key with its private key and acknowledges receipt, initiating an encrypted session.
5. Both the server and browser encrypt all data transmitted using the session key.
1. The browser connects to an SSL-secured web server and requests identification.
2. The server sends its SSL Certificate, including the public key.
3. The browser encrypts and sends a symmetric session key back to the server using the public key after checks the certificate with trusted CAs for validity.
4. The server decrypts the session key with its private key and acknowledges receipt, initiating an encrypted session.
5. Both the server and browser encrypt all data transmitted using the session key.


Web Browser
Web Server
SSL Certificate Comparison
SSL certificates come in different varieties, each designed to address specific levels of security, trust, and validation requirements.
SSL Certificate Comparison
SSL certificates come in different varieties, each designed to address specific levels of security, trust, and validation requirements.
EV
(Extended Validation)
- Highest cost
- Maximum trust
-
Validation Time:
1-5 business days
-
Requires legal and physical business verification, including company documents.
-
Financial institutions, large e-commerce platforms, government websites.
Recommended
OV
(Organization Validation)
- Moderate cost
- High trust
-
Validation Time:
1-3 business days
-
Requires verification of domain ownership and organization identity.
-
Business websites, SaaS platforms, and internal systems.
DV
(Domain Validation)
- Lowest cost
- Basic trust
-
Validation Time:
Minutes to hours
-
Only requires proof of domain ownership via email or DNS.
-
Personal blogs, informational sites, or basic websites
Comparison of Wildcard SSL and Normal SSL Certificates
Comparison of Wildcard SSL and Normal SSL Certificates
Wildcard SSL
-
Secures the main domain and all subdomains.
-
Can be issued with DV or OV validation.
- Ideal for websites with multiple subdomains.
-
High for subdomain encryption but does not display organization details.
-
Higher than standard DV or OV certificates but covers multiple subdomains.
Normal SSL
-
Protects a single domain or subdomain.
- validation varies based on the type of SSL
- For
high-security websites,
business websites or
personal or small-scale websites.
-
Different Trust Level based on different SSL
-
Different cost based on different SSL
Comparison of Wildcard SSL and Normal SSL Certificates
Comparison of Wildcard SSL and Normal SSL Certificates
Wildcard SSL
-
Secures the main domain and all subdomains.
-
Can be issued with DV or OV validation.
- Ideal for websites with multiple subdomains.
-
High for subdomain encryption but does not display organization details.
-
Higher than standard DV or OV certificates but covers multiple subdomains.
Normal SSL
-
Protects a single domain or subdomain.
- validation varies based on the type of SSL
- For
high-security websites,
business websites or
personal or small-scale websites.
-
Different Trust Level based on different SSL
-
Different cost based on different SSL
FAQ
What is SSL?
SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) is a security protocol that encrypts data between a web server and a browser, ensuring that sensitive information like passwords and payment details remains private and secure.
An SSL certificate protects your website and users by encrypting data, boosting trust with a padlock icon, improving SEO rankings, and ensuring compliance with industry security standards.
What are the different types of SSL certificates?
EV SSL (Extended Validation): Maximum validation, ideal for high-security sites.
OV SSL (Organization Validation): Verifies organization identity, suitable for businesses.
DV SSL (Domain Validation): Basic validation, best for small websites or blogs
How do I know if a website has SSL?
You can check if a site has SSL by looking for "https://" in the URL.
To see more details, click on the site information icon (🔍 or "Not secure" text) in the browser’s address bar.
If the site is not secure, the browser will display a warning.
What happens if I don’t have SSL?
Without SSL,
your site may display a "Not Secure" warning in browsers
lose user trust
risk data breaches
resulting in lower search rankings & fewer visitors
How do I install an SSL certificate?
- Purchase and Generate
Buy an SSL certificate from a trusted provider or use a free service like Let’s Encrypt. Generate a CSR (Certificate Signing Request) on your server, which contains your domain and organization details.
- Verify Domain
Complete the SSL validation process. Depending on the SSL type, this could be done via email confirmation, adding a DNS record, or uploading a file to your website.
- Download Certificate
Once issued, download the SSL certificate files, including the primary certificate, intermediate certificate, and root certificate, from your provider's dashboard.
- Install SSL
Use your hosting control panel (e.g., cPanel or DirectAdmin) or manually upload the certificate files to your server and configure the web server (e.g., Apache or Nginx).
- Test and Force HTTPS
Test the installation using tools like SSL Labs to ensure it’s working. Redirect all traffic to HTTPS to secure your site fully.
What is the difference between SSL and TLS?
TLS (Transport Layer Security) is the successor to SSL. It’s more secure and modern, but the term "SSL" is still widely used to refer to both protocols.
What is a Wildcard SSL Certificate?
A Wildcard SSL Certificate is a type of SSL certificate that secures a domain and all its subdomains under a single certificate. For example, if you purchase a Wildcard SSL for example.com, it will also cover:
www.example.com
mail.example.com
blog.example.com
This makes it cost-effective and convenient for managing multiple subdomains.
What is the different between Wildcard SSL Certificate and DV,OV,EV SSL?
Wildcard SSL is focused on securing multiple subdomains, while EV, OV, and DV SSL are primarily about the level of validation and trust provided for a single domain.
Choose Wildcard SSL if you have multiple subdomains to secure, or stick with EV/OV SSL if trust and verification are priorities.

